Object security
Object Security Principles
Object security is used to set user access permissions to objects in the tree. Permissions can be enabled, disabled, or combined in various ways. These settings are made in ALVAO WebApp - Administration in user management
in the Object Security block, or on individual objects in the AM Console (only the Asset System Administrator can change them here).
In order for the rights settings in the object tree to take effect, the Use rights in object tree option must be checked in the Asset Management settings - see Global Settings. Enabling this option causes no objects to be displayed to users who have no permissions defined in the object tree. Objects will only be displayed when the Read permission is enabled. The exception to this is a user with the Administrator role for ALVAO Asset Management, to whom the tree permissions are not applied (all objects in the tree are always displayed).
Rights
The system allows you to set 5 types of permissions:
| Permissions |
Description |
| Read |
The user sees the object in the object tree. |
| Change |
The user can change the properties and property values of the object. |
| Move |
The user can move the object to objects in which the object being moved will also have this right. For example, if the right is set for object type Mobile Phone on the Department A and Department B folders, mobile phones can be moved within and between departments. |
| Remove |
User can delete an object. |
| Create arbitrary objects |
User can create new child objects of any type under the defined object. |
Caution:
Permissions can be granted or denied. Denying permissions takes precedence over granting permissions.
Note:
The default setting for all objects and permissions is
deny - that is, the user does not see any objects in the object tree until they are allowed to read them.
Note:
Object security can be set for a group of users.
When permissions in the object tree are disabled, system roles have the following permissions in the tree:
| Role |
Read |
Change |
Move |
Remove |
Create arbitrary objects |
Note |
| Administrator Asset Management |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
Cannot restrict rights in tree |
| Reader |
x |
|
|
|
|
|
| Asset manager |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
| Software Licence Report |
x |
|
|
|
|
Same as Reader |
| Hardware and Software Detection Report |
x |
|
|
|
|
Same as Reader |
| Accountant |
x |
x1 |
|
|
|
Can change values of some properties |
| Link reader |
x |
|
|
|
|
Same as Reader |
| Links Report |
x |
|
|
|
|
Same as Reader |
1 The Accountant role can change the values of properties if you have this option in the Property Definition window on the Security set.
Caution:
When rights are enabled in the object tree:
- Implicit rule - everything that is not enabled is disabled.
- A command rule over an object (except the default rule) takes precedence over an enable rule, even for inheritance to child objects.
- Read permissions are evaluated from the root of the tree, i.e. an object will not be displayed to the user unless all its parent objects also have read permissions.
- The order in the rules table has no effect on their evaluation. All of them are always evaluated with the limitations listed above.
Note:
Each user in the ALVAO WebApp can see own assets, i.e. they has the right to read on all child objects under their person in the tree.
Note: Membership in an AM user group is not an alternative for securing objects. If users are to modify, move, create, and delete objects, they must be members of the Property Rights group and must also define which objects these rights apply to.
Example: How to set rights for the Mobile Phone Administrator group
In this example, we create a new group
Cell phone managers business and set permissions on it so that members of this group will take care of cell phones in the
Business Department. They should have the right to work with objects of type
Cell Phone:
- Create (stack) them under the Warehouse object.
- Edit their data anywhere in the entire tree.
- Move them from the warehouse to anywhere under the Business Department object (and back again if necessary).
- Group members cannot see other departments.
Example object tree structure:
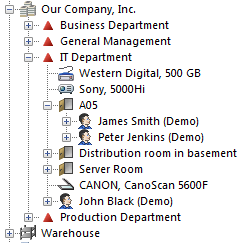
- Go to the ALVAO WebApp and make sure that the object tree rights are enabled - enable the Use object tree rights option in Management - Asset Management - Settings -
General.
- Create a new group called Cell phone managers business.
- Edit the group, in the Is a member section, add the Cell phone companies group.
Asset managers. In the Object Security section, set permissions according to the following table:
| Object Type |
Object Name |
Including subtree |
Objects of type |
Read |
Change |
Move |
Remove |
Create arbitrary objects |
|
|
No |
Cellular phone |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
|
| Object templates |
Object templates |
No |
|
Yes |
|
|
|
|
| Folder |
IT Assets |
No |
|
Yes |
|
|
|
|
| Warehouse |
Warehouse |
No |
|
Yes |
|
|
|
Yes |
| Warehouse |
Warehouse |
Yes |
Cellular phone |
|
|
Yes |
|
|
| Organization |
Our Company, Inc. |
No |
|
Yes |
|
|
|
|
| Department |
Business Department |
Yes |
|
Yes |
|
|
|
|
| Department |
Business Department |
Yes |
Cellular phone |
|
|
Yes |
|
|
Note:
On the
Business Department object, we have set that the user can move and change objects of type
Mobile in it. This right will also allow the user to move objects under this department, but at the same time they cannot move the whole department, only the mobile phones lying inside the department.
- Add user Joseph Freeman (Demo) to the newly created group Cell phone managers business - edit the user and add the appropriate group on the Is a member tab.
- When the user Joseph Freeman (Demo) then logs into the AM Console,
the object tree will look like this:
Did not find what you were looking for? Ask our technical support team.