Relations
To keep track of the relations between the records of each ITIL process, we recommend using the following types of relations:
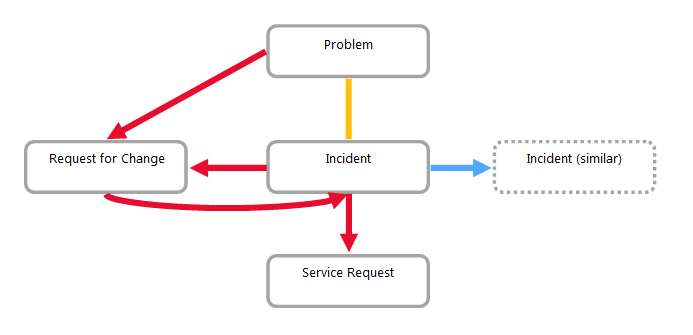
For "simple" ITIL, we recommend recording all relations as "related."
If you want to implement ITIL more consistently, we recommend using the following types of relations:
| ITIL |
Relation Type |
Note |
| Incident - similar Incident (parent - child) |
duplicated - duplicate |
The first incident is marked as "duplicated". All other incidents related to the same fault are duplicated.
|
| Incident - Problem/Known Error |
related |
An incident may occur to an existing problem. A problem can arise from an existing incident. For this reason, it is not appropriate to use "preceding - following".
|
| Incident - Service Request |
preceding - following |
Service Request is created and based on an incident (SR handles the incident).
|
| Incident - RFC (N:N) - RFC is triggered by an incident |
preceding - following |
RFC resolves an incident.
|
| RFC - Incident (caused by) |
preceding - following |
Incident caused by a poorly executed change.
|
| Problem - RFC |
preceding - following |
The problem is solved via an RFC.
|
Did not find what you were looking for? Ask our technical support team.