Filter
You can use the filter to display only those rows in the table which comply
with certain criteria. The commands for the filter are grouped in the table
context menu and in the header context menu.
If the filter is enabled, the filter parameters are displayed in the row
below the table header. 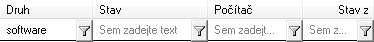 You can
enable and disable the filter with the - Filter
command in the table header context menu.
Filter By Selection
This command is convenient, if your table contains too many rows and you are
only interested in some of them. Some tables (tabs) can contain item lists of
considerable length. You can right-click on a specific item and select
Filter By Selection from the context menu. This will enable a filter in
the table which will only display the rows containing the selected value.
For example, the Detection tab in the
Main Window main contain a long list of various detections. If you are only
interested in software detections, i.e. the rows with the "software" value in
their "Kind" columns, you can find a single software detection row, right-click
on the value in the "Kind" column and select - Filter By Selection in the
context menu. This will enable a filter which will filter out all entries that
do not contain the value selected in the "Kind" column.
Note: The command
Filter By Selection can be located in the
Table submenu.
Filter Excluding Selection command
This command is used in a way that is similar to the
Filter By Selection command. The difference between these two filters is
that the second filter will filter out all rows with the selected value in their
rows. All other rows will be displayed.
Advanced filter
If a filter is enabled, you can adjust its settings manually in the row below
the header. If you enter some text into any column, the table will only display
those rows, whose value in its respective column contains the text string you
have entered. Diacritic characters are ignored.
The asterisk character
replaces any number of any characters. For example, if you type "ar", the filter
will only display values that contain the "ar" sub-chain. Entering "*ar*" would
give you the same result, because the asterisk is attached to the beginning and
to the end of each text string automatically.
You can also use the row
below the header to enter a Boolean expression, e.g:
"*ar*" or "*unk*"
The parts of the text that you are searching for must be enclosed
in inverted commas. The expression can use the following operators:
The keywords provided in the table below can only be used in
filters for columns with Yes/No (Boolean) values:
If the column is a number, you can use mathematic operators ">"
(greater than), "<" (less than), ">=" (greater than or equal
to), "<=" (less than or equal to), "!,Not,<>,!=" (negation, not
equal to), "=,==" (equal to).
Filter for Column Type "Date and Time"
If the column is the "date and time" type, the following filter string forms
are supported:
- now – displays all records for the current
day and time with a tolerance of +- 2 hours.
- today – displays all records for today.
- *.M.YYYY – displays records for month M and
year YYYY
- *.*.YYYY – displays records for year YYYY
- D.M.YYYY – displays records for a specific
day D.M.YYYY
- D.M.YYYY H – displays records for a
specific day D.M.YYYY and hour H
- D.M.YYYY H:M – displays records for a
specific day D.M.YYYY, hour H and minute M
- operators:
| Operator |
Description |
Example of use |
| <, >, <=, >= |
less than, greater than, less than or equal to,
greater than or equal to |
>15.4.2013 |
| =, == |
equal to |
=15.4.2013 |
| !=, <> |
not equal to |
<>15.4.2013 |
| Not, ! |
negation (same meaning as not equal to) |
Not 15.4.2013 |
| and, or |
logical multiply and logical sum |
=15.4.2013 or =16.4.2014 |
Note:
- Dates can use the following formats to specify dates in your
filter: D.M.YYYY, M/D/YYYY, and
YYYY-M-D. Date separators can be followed by a space,
months can be specified as single-digit or double-digit numbers,
years need to be specified as four-digit numbers.
- If you use the AND or OR
operator, the dates around the operator need to contain a
mathematical operator (e.g. =).
Examples
- Show data for the current day:
today
- Show data for 4/14/2014:
14.4.2014
- Show data for 10/24/2013, 3 p.m.:
24.10.2013 15
- Show data for March 2014:
*.3.2014
- Show data for 2013:
*.*.2013
- Show data for the period between January and May 2013:
>=1.1.2013 and <1.6.2013
- Show data for 10/5/2013 and 10/6/2013:
=5.10.2013 or =6.10.2013
@me variable
@me variable represents the name of the user who is currently logged in. You
can use it for filtering out the records related to the user who is currently
logged in. This variable is available only in the ALVAO Service Desk –
Requests where you can use it in the Requester and Solver columns.
Did not find what you were looking for? Ask our technical support team.
|