Links between requests
Request links to other requests are shown on the Request page -
Links tab. You can also view the links directly in the requests table.
Types of links
| Link type |
Link meaning |
Relates to
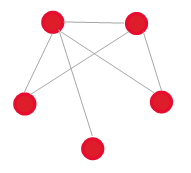 |
For example, two change requests are for the same device (CI). These requests are related.
This is a general type of link. There is no functionality tied to this link type.
|
It is parent over / It is child under
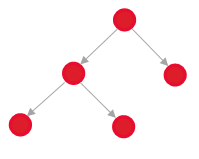 |
For example, a supervised task consists of sub subordinate tasks (decomposition).
A parent request cannot be closed while it has open child requests.
A notification is automatically sent to the solver of the parent request when each child request is resolved.
|
Precedes before / Follows after
 |
For example:
- Previous tasks must be completed chronologically before next tasks.
- The following request was created based on the preceding request.
Used to document the solution sequence or origin of the request.
|
Blocking/Is Blocked
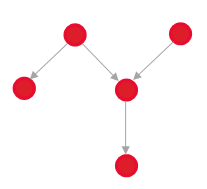 |
For example, a blocked request can only be started or completed after the blocking request is complete.
Note: The application does not restrict the resolution or closure of a blocked request in any way.
A notification is automatically sent to the solver of the blocked request when each blocking request is resolved.
|
Is Duplicated / Duplicating
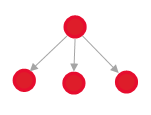 |
For example, two users have reported incidents regarding the same issue. The first incident will be Duplicated, the second will be Duplicate to it.
|
ITIL
For links between records of individual ITIL processes, we recommend using the following types of links:
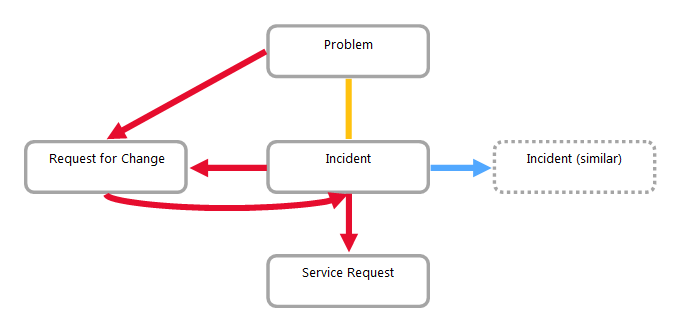
For "simple" ITIL, we recommend recording all links as "related".
If you want to implement ITIL more consistently, we recommend using the following types of links:
| ITIL |
Link type |
Note |
| Incident - similar Incident (parent - child) |
Is Duplicated - Duplicates |
The first incident is marked as "Is Duplicated". All other incidents related to the same fault duplicate the first incident. |
| Incident - Problem/Known Error |
Related to |
An incident may occur to an existing problem. A problem can arise from an existing incident. Therefore, it is not appropriate to use "Precedes Before - Follows After". |
| Incident - Service Request |
Precedes Before - Follows After |
Service Request is created based on an incident (SR handles the incident). |
| Incident - RFC (N:N) - RFC is triggered by an incident |
Precedes before - Follows after |
The RFC resolves the incident. |
| RFC - Incident (caused by) |
Precedes Before - Follows After |
Incident caused by a poorly implemented change. |
| Problem - RFC |
Precedes before - Follows after |
Problem is resolved via RFC. |
Custom link types
The Alvao administrator can create custom link types in the database in the TicketRelationType table. Changes to system link types are not supported.
Tip:
When creating new link types, choose the start and end of the link so that the link is mostly created from the initial request. When creating a link, the end names of all types are offered first, then the start name.
Did not find what you were looking for? Ask our technical support team.