Asset Management and Service Asset and Configuration Management
Objects tree in ALVAO Asset Management can be divided in different ways.
- Organizationally
- Example: Company -> Division -> Department -> Center
- Locally
- Example: Company -> City -> Building -> Floor -> Room
Both approaches have their advantages and disadvantages. The correct choice of tree structure is influenced mainly by these factors:
- Tree clarity
- Solver team should quickly assess from the position of an object in the tree, what it is and what the context is.
- Often it also shows the impact whether it is just a local printer or a shared one).
- Privileges within the Tree
- The organizational structure allows setting the permissions to see the data in WebApp for Managers by Department, Division, etc.
- Local structures help solver team in cases when the managed devices are deployed in multiple locations and there is a need to give different privileges to different technicians at these locations.
- Inheritance within the Tree
- Correctly designed tree facilitates filling in the information.
- There is no need to fill in the information such as department numbers, employee names then and these information is spread automatically throughout the tree.
Practice shows that both approaches can be blended together in case of need. The whole tree can be based on an Organizational division and then in case of need go smoothly into Local division. Any change in the tree organization is possible in the future and it does not mean that you will have to enter the information again. 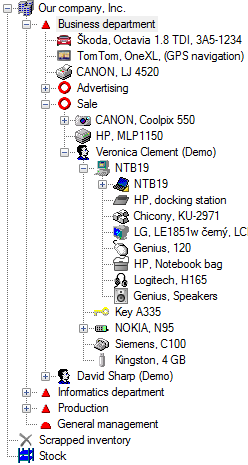 Life Cycle
Life cycle of each object (CI) is historically noted in the log of each object. It can be registered in two ways:
- By the position in the tree (recommended)
- By the "Status" property
Life Cycle Management Using the Tree PositionRight after installation there in the system are the following system folders ready: Warehouse, Disposed assets, Recycle bin. These folders can be advanced in case of need with the following additional folders: Assets to Dispose, Complaints (this can be further divided by vendors), Installations, etc. The position within the tree then simply shows where the given object currently is, which represents its status at the same time. The user can perform the changes of status by simple drag&drop operations within the tree.
Example of Position within the Tree Usage:
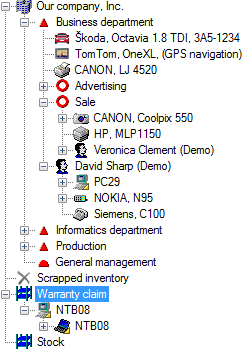 Life Cycle Management Using "Status" PropertyThe "Status" property is edited manually during the object life cycle (more difficult in terms of administrative). However this way can be used well for objects representing important servers or key applications on which a rigorous Release Management is performed.Example of "Status" Property Usage:
Stocktaking
See ALVAO Asset Management – Asset Stocktaking Workflow.
Example of internal guidelineInternal guideline regarding this issue should contain the following information:
- Computers and other IT devices assigned to users are administered in ALVAO Asset Management.
- Each user can find a list of devices assigned to him/her on https://server/asset.
- If the employee finds discrepancies in the register, he/she reports this immediately to the Service Desk.
Did not find what you were looking for? Ask our technical support team.
|