Links Between Requests
Request links are displayed on the page with request details, tab "Links". Links tab is displayed in the request detail to users who have the operator, solver, irregular solver, or manager role at least on one service in SD. The individual lines contain the link type and number, as well as the name of the linked request. For example, the line "Is blocked by T123ALVAO" should be interpreted like this: "The selected request is blocked by request number 123." You can use the Add, Remove and Edit buttons to work with links. Before you remove or edit an item, use the checkbox in the field on the left to select the item that you want to remove or edit.
The "Show tree of child requests" link opens a new window with a tree of requests with the Is the parent of / Is the child of links where the selected request is located.
The "Display in window" command opens a window with a new list of requests. This window will only list requests from the "Links" tab.
The following link types are defined in the basic database:
| Source Request |
Link Meaning |
| Relates to |
Generic link type.
This link type has no functionality. |
| Is the parent of / Is the child of |
The meaning corresponds to the links between the project tasks. A parent request consists of child requests.
Parent requests cannot be closed if they include open child requests. |
| Precedes before / Follows after |
The meaning corresponds to the order of creating requests in corporate processes. The request was created based on a different request.
It documents the request origin and solving process. |
| Blocks / Is blocked by |
The meaning corresponds to the links between the project tasks. A blocked request is dependent on the request which it is blocked by. Blocked requests can be solved or finished only after the blocking request has been finished.
Note: The resolving or closing of a blocked request is in no way limited by the application. |
| Is duplicated by / Duplicates |
A request which duplicates request A is the same as request A. |
You can create custom link types that are written to the database table TicketRelationType. Predefined link types cannot be edited.
Tip: If you want to create new link types, select the link beginning and end to allow new links to be created from original requests in most cases. When creating a new link, you will be offered the end names of all types first and the initial names second.
Related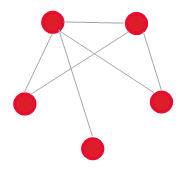 Example: Two change requests concern one and the same CI. The relation of these requests is as follows.
Previous – Next 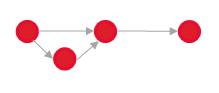 Example: Previous tasks must be completed before next tasks can be worked on.
Parent – Child 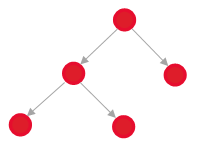 Example: The parent task consists of partial child tasks (decomposition).
Duplicated – Duplicate
Example: Two users submitted incidents concerning the same problem. The first incident will be Duplicated, the second Duplicate.
If the link is used for full duplicity, this will create trees with a depth of 2: 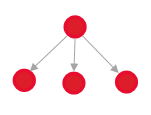 If the link is set up also for partial duplicity, this will create a more complex graph:  ITIL
We recommend using the following link types for relations between the records of individual ITIL processes: 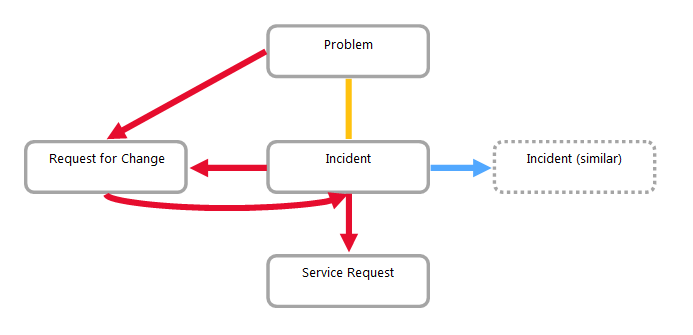 All links for "simple" ITIL should be recorded as "related".
If you want to implement ITIL more rigorously, we recommend using the following link types:
| ITIL |
Link Type |
Note |
| Incident – similar Incident (parent – child) |
Is duplicated by – Duplicates |
The first incident is marked as "Is duplicated by". All other incidents relating to the same problem are duplicating the first incident. |
| Incident – Problem / Known Issue |
Relates to |
The incident can be created for an existing problem. A problem can be created based on existing incidents. It is therefore not recommended to use Precedes before – Follows after. |
| Incident – Service Request |
Precedes before – Follows after |
The Service Request will be created based on an incident (SR is involved in an incident). |
| Incident – RFC (N:N) – RFC is triggered by an incident |
Precedes before – Follows after |
RFC is involved in an incident. |
| RFC – Incident (caused by) |
Precedes before – Follows after |
The incident was caused by a change made incorrectly. |
| Problem – RFC |
Precedes before – Follows after |
The problem is being solved through RFC. |
Working With Links
You can use the Request Details page to add, edit and delete links. The Request Details page contains the Links tab with an overview of current links within the request. You can use this tab to process the links further. The number in the parentheses on this tab shows how many links there are in the current request.
If you want to work with existing links, you need to select the required links by selecting the appropriate checkboxes on the left.
The View parent/child requests command will open a new window with a tree of requests with the Parent/Child links where the current request is saved.
The Display in window command will open a window with a new list of requests. This window will only list requests from the Links tab.
Note: Starting with ALVAO 7.0, the "Parent – Child" relation has replaced the system of sub-requests known from ALVAO 6.0. When you upgrade from a legacy version, all sub-requests will be automatically converted to the "Is the parent of – Is the child of" relation.
Did not find what you were looking for? Ask our technical support team.
|